We associate mycosis primarily with painful changes in the skin and nails. However, it is worth knowing that it can also affect internal organs. The development of a fungal infection of the respiratory tract is especially dangerous. This can cause pneumonia, severe shortness of breath, and even lung infarction. The disease very often indicates a decrease in immunity, problems with the immune system, as well as chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus. Check how it manifests itself, what are its causes and what treatment.
What is mycosis of the lungs, and what are its causes?
Lung fungus is a dangerous infection caused by fungal spores that are common in soil, air, and water. They are favored by humidity and limited oxygen supply. Fungal spores enter our body through the respiratory, digestive and skin systems. Mold infestation can cause conjunctivitis, joint pain, and respiratory problems. However, mycosis of internal organs almost never develops in people with a properly functioning immune system. Then the spores of the fungi do not cause us much harm and are quickly neutralized.
The most common causes of pulmonary mycosis are congenital and acquired immunodeficiency (HIV, AIDS), disorders of the immune system due to cancer and chemotherapy, and a state of immunosuppression, that is, suppression of the immune system using pharmacological agents to prevent transplant rejection.
Premature babies and people with serious chronic diseases (for example, severe circulatory failure, advanced diabetes and respiratory diseases) are also much more likely to suffer from mycosis. The most common causes of infection are Candida albicans and Aspergillus. The use of catheters and artificial heart valves is also a risk factor.
Symptoms of mycosis of the lungs
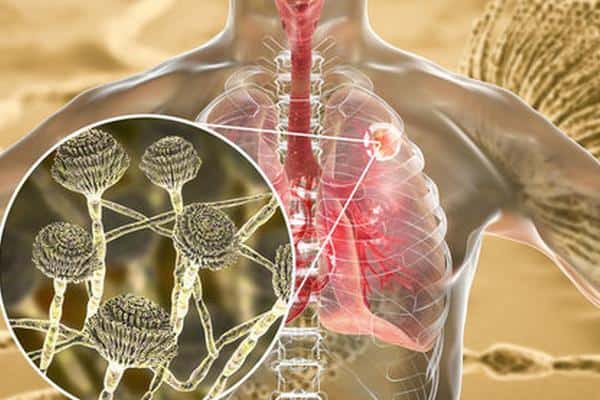
Lung mycosis is very often confused with other respiratory infections. It is difficult to distinguish it from bacterial pneumonia in symptom-based symptoms. Symptoms include high fever, a deep and moist cough, shortness of breath, chest pain that worsens with coughing, and thick discharge from the airways. Some patients also develop hemoptysis.
Therefore, the key difference between infections may be the general condition of the patient – frequent infections, the coexistence of diabetes and other chronic diseases may indicate immunodeficiency. This, in turn, indicates a fungal infection. Infection with asperite affects both lungs and resembles tuberculosis. In every third case, the disease spreads to other organs.
Diagnosis and treatment of mycosis of the lungs
Diagnosis of mycosis of the lungs is a chest x-ray and tomography. They allow you to detect the characteristic shadows of the parenchymal and fibrosis, most often in the lower lungs. However, the most effective test is a fine-needle biopsy of the lung. Blood tests are also helpful to determine the presence of fungal antigens.
Treatment consists of taking medication for at least several weeks. Some patients require surgical removal of a portion of the lung that is infected with Aspergillus.








