Зміст
Rheumatism is the general name for a group of inflammatory diseases, which include diseases of the muscles, joints, and bones. The most common symptoms of rheumatic diseases are joint pain and swelling, stiffness and limited mobility. Untreated rheumatism can lead to significant mobility impairment. What does rehabilitation look like for rheumatoid diseases?
What is rheumatism?
Rheumatism is a colloquial term for about 200 diseases affecting the musculoskeletal system, mainly the joints. Despite the different accompanying symptoms and course, all rheumatic diseases are characterized by chronic, recurrent rheumatic pain and impaired mobility in various joints of the body. Rheumatism refers to inflammatory changes in connective tissue. It occurs in both older and younger people, regardless of gender. According to statistics, every fourth person in Ukraine suffers from it.
Too late diagnosis and untimely initiation of treatment and rehabilitation can lead to irreversible changes in the musculoskeletal system, which will actually complicate independent functioning and professional activity, leading to significant disability over several years.
Rheumatism – causes
The cause of rheumatism is not fully known. Its appearance and development can be influenced by both external, environmental and genetic factors (rheumatism can also be hereditary).
Factors that cause rheumatic diseases include: vitamin D and calcium deficiency, little or too much physical activity that overloads the joints, poor diet, prolonged exposure to damp and cold environments (cold rheumatism), untreated childhood diseases (angina or postural rheumatic disease). Defects) causing rheumatism in children), viral diseases or endocrine disorders.
Rheumatic pain in the legs, rheumatism in the arms and accompanying fatigue can also depend on the weather. However, the main cause of rheumatic diseases is abnormal autoimmune reactions of the body, which produces substances that damage its own tissues.
Rheumatism – symptoms
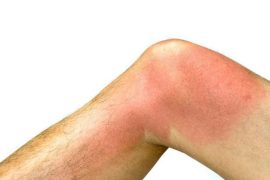
It should be noted that the symptoms of rheumatism periodically worsen and disappear. The joints are usually affected, resulting in pain (especially in the morning) and decreased mobility. Rheumatism can impact the fingers, wrists, knees, hips, and even the joints of the spine.
With rheumatism, the synovial membrane in the joints is destroyed, which contributes to the development of inflammation with swelling and fluid leakage into the joint. The skin in such a place is often red and warm, and the joint itself loses elasticity and mobility, and bone growths and deformities may also appear. People suffering from rheumatic diseases typically experience loss of appetite, difficulty falling asleep, muscle pain and low-grade fever. Such illnesses can also lead to depression. Degenerative changes that occur in the joints are most typically irreversible, and rheumatism itself also impacts muscles and soft tissues.
Symptoms associated with rheumatism may be worsened by severe stress, changes in diet, other underlying medical conditions, or viral and bacterial infections. They should never be ignored, since complications associated with the disease can be very dangerous for the patient.
Rheumatism – diagnosis
Diagnosis of rheumatic diseases is quite complex and requires consultation with a rheumatologist. Useful and often recommended tests for rheumatism include urine and blood laboratory tests, immunological tests, X-rays, CT scans, and magnetic resonance imaging. Laboratory tests typically reveal a high ESR and an increased concentration of so-called acute phase proteins, and a decrease in the number of leukocytes. Anemia also occurs. Histopathological tests can also be useful in diagnosing rheumatic diseases.
The course of treatment and the patient’s health condition depend on a quickly made correct diagnosis. Rheumatism can also occur in young people, which is why it is so important not to ignore the first signs of the disease.
Rheumatism – treatment
Treatment of people suffering from rheumatic diseases is a comprehensive program combining pharmacology, diet, and rehabilitation. Although rheumatic diseases have no cure, quickly administered therapy can radically reduce pain, improve quality of function and slow the progression of the disease.
The most commonly used drugs for rheumatism are painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids and drugs that modify the course of inflammatory forms of rheumatoid diseases. Rheumatism tablets should always be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
Diet and rheumatism also go hand in hand. The joint diet should be low in sweets, fatty meats, offal, potatoes, peas, soybeans, spinach and green peas, as well as vinegar, mustard, and pepper. However, it is recommended to eat plenty of vegetables, fruits, olive oil and sea fish.
Treatment of rheumatism should be supplemented with psychotherapy, which will help you get used to the disease and learn to cope with pain and stress associated with rheumatic changes.
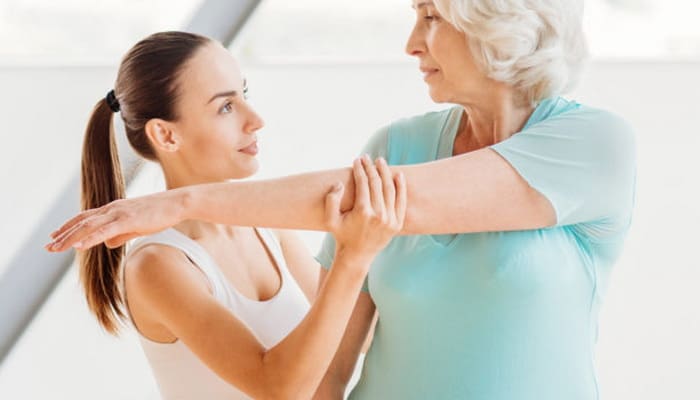
Rheumatism – physiotherapy for rheumatic diseases
Physiotherapy for rheumatic diseases is a complex combination of physical activity and exercises with physiotherapy and massages. Physiotherapy treatments include heat and cold therapy, ultrasound therapy, magnetic therapy, diathermy, laser therapy and balneotherapy. At home, you can use mud compresses for joint pain. Home remedies to treat and relieve rheumatic pain also include compresses made from arnica montana, camphor oil, and even cabbage leaves.
Rheumatism – exercises for rheumatism and hand diseases
- Place your hands palm-side down on the table. Change the position of your hand once to the back side and then back to the palm side. Repeat 10 times.
- Place all hands on the table. Raise only your fingers without lifting your palm from the table. Repeat 10 times.
- Place one hand and forearm on the table, resting on the outer edge (little finger touching the table and thumb pointing up). Use your other hand to hold your forearm to prevent it from moving during the exercise. Raise your hand above the table with your thumb facing you. Repeat 10 times.
- Position as above. Close your fingers and spread them outward. Repeat 10 times.