Зміст
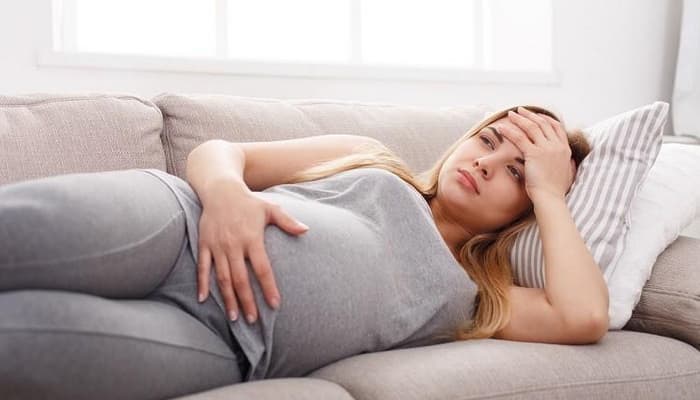
During the third trimester of pregnancy, dizziness occurs due to pressure from the uterus on important blood vessels and increased energy needs. At all stages of pregnancy, dizziness can be a consequence of gestational diabetes or gestational anemia. Early in pregnancy they occur as a result of hormonal changes.
In addition to dizziness during pregnancy, women expecting a baby often suffer from headaches of various origins. This could be tension pain, migraine pain that occurs as a result of too low blood pressure. Women who have not suffered from migraines may experience them during pregnancy. Migraine attacks during pregnancy account for almost 90% of all headaches during this period.
Dizziness as a symptom of pregnancy, causes of dizziness in early pregnancy
One of the first symptoms of pregnancy is dizziness. They occur because the woman’s body adapts to a new situation, causing confusion in hormonal management. Dizziness at the beginning of pregnancy is due to the fact that more blood circulates in the uterus and its surroundings than before conception. Dizziness in early pregnancy usually occurs due to sudden changes in position. They occur especially typically when a pregnant woman suddenly gets up from a sitting or lying position.
Another cause of dizziness at the beginning of pregnancy is a drop in blood pressure. Progesterone, the level of which increases significantly in early pregnancy, causes the walls of blood vessels to relax. This is a direct cause of low blood pressure and an indirect cause of dizziness.
Dizziness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy: anemia and hypoglycemia
Dizziness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy can be a consequence of too low and/or high blood sugar levels. A glucose tolerance test is performed between 24 and 28 weeks to detect gestational diabetes. This type of diabetes appears during pregnancy and disappears after childbirth. Untreated gestational diabetes can cause birth defects in the fetus and also have negative effects on the mother. The most dangerous thing with gestational diabetes is hypoglycemia, i.e., low blood sugar. This is a drop in blood sugar levels below 70 milligrams per deciliter. Hypoglycemia during pregnancy can even lead to coma or death of the woman.
Dizziness during pregnancy in the 2nd trimester can also be a symptom of persistent gestational anemia. Too low hemoglobin and hematocrit values in combination with iron deficiency cause weakness, dizziness and headaches, increased fatigue, chronic fatigue and problems with concentration, as well as pale skin and attacks of shortness of breath. Anemia in pregnancy can lead to miscarriage and increases the risk of birth defects and fetal growth restriction.
Causes of dizziness during pregnancy in the 3rd trimester
Dizziness during pregnancy occurs most often in the 3rd trimester, considering the entire period of pregnancy. They can be a symptom of gestational diabetes or gestational anemia, but usually result from increased energy demands and physical pressure on the blood vessels.
Dizziness is common in the third trimester of pregnancy, which can be dangerous if it ends in fainting. A fall puts the health and life of both mother and child at risk. If they occur frequently, consult your doctor.
Already 3 months before birth, the fetus is so large that it puts pressure on the blood vessels, sometimes disrupting proper blood flow. Symptoms intensify when sleeping on the right side and with a sudden change in body position. While sleeping or lying on the right side, the woman takes a position that favors the pressure of the uterus on the inferior vena cava.
Fetal growth requires the provision of an adequate amount of energy. If your diet is too low in calories or minerals and vitamins, you may feel dizzy. A factor contributing to fainting during pregnancy in the third trimester is persistent anemia resulting from iron deficiency.
Ways to combat dizziness during pregnancy and prevent fainting
Severe dizziness during pregnancy accompanied by fainting or symptoms of gestational diabetes or gestational anemia should require consultation with your doctor and possibly a dietitian.
Recommended Products:
- rabbit, turkey, lean beef and veal,
- multigrain products,
- cereals,
- vegetable fats,
- skim milk and products made from it,
- thick cereals,
- fresh vegetables and fruits high in vitamin C, such as oranges, black currants, red peppers.
During pregnancy, it is best to avoid eating sweets, salty snacks, fatty meats and animal fats, as well as drinking large amounts of coffee and sugary carbonated and non-carbonated drinks. Fast food is also not recommended, including French fries, pizza, kebabs, hamburgers and hot dogs.