Зміст
Eczema is an inflammation of the skin. It most often occurs in people who work manually, who may come into contact with substances that irritate the skin. Eczema is a disease that is not transmitted by contact with an infected person.
Eczema is an inflammation of the skin that can be caused by many factors. These can be internal causes, such as genetic predisposition, as well as external causes, such as contact with skin irritants or allergens. The main symptom of this disease is swelling, redness and itching of the skin.
Eczema on the hands causes
Eczema on the hands can be called an occupational disease. People who are in daily contact with substances that irritate the skin are especially prone to it, that is, people who clean or wash dishes, as well as catering workers, hairdressers, medical workers, car mechanics, etc.
Eczema can occur. Be an allergic reaction of the body to substances contained in detergent, cosmetics, solvents, and plastics in clothing. Spots on the skin can be caused by metals from which jewelry is made, for example, nickel. In addition, food ingredients can cause eczema.
Types of eczema
Eczema can be divided into two types:
- contact eczema – if it is caused by contact with irritating substances contained in everyday objects or materials used at work, for example, oil, cement, or shampoo; it can be allergic contact dermatitis;
- atopic dermatitis – the most common form of this disease, caused by internal factors, for example, allergic predisposition to the disease; along with this, additional allergy symptoms such as hay fever, dry cough, wheezing, or shortness of breath may be observed.
Eczema symptoms
Eczema is manifested by the formation of red bumps or spots on the skin. Over time, burst bubbles filled with pus begin to appear on their surface. In the later stages of the disease, scabs from dried secretions remain on the skin. Regardless of the type of eczema, additional symptoms may include swelling, itching, or loss of skin elasticity. Do not scratch the wound, as this can lead to scarring, discoloration or discoloration of the skin, and thickening and hardening of the epidermis.
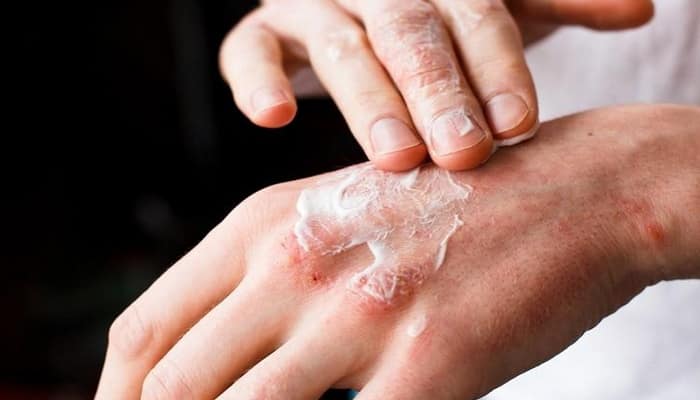
Eczema on the hands – home remedies
The way to reduce the symptoms of eczema on your own is to exclude allergenic ingredients from your diet. Allergy tests can be performed to determine the factor that should be eliminated, or in the case of less severe symptoms, allergenic food ingredients can be ruled out with provocation tests. In addition, stimulants such as coffee, tea, alcohol, etc., which can increase symptoms, should be avoided. Instead of these drinks, you should add infusions of clover and nettle, decoctions of burdock root or any mixture of these herbs. To relieve itching of the skin, you can use aloe juice compresses, which have a softening and soothing effect.
Skin care for eczema
Manuka honey is also effective in treating eczema due to its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and disinfectant properties. Aspects of everyday behavior are also important – you should abandon rough and therefore irritating skin underwear, avoid sudden temperature changes, limit contact with animals, avoid sunlight (especially in spring and summer), dress warmly in winter and wear gloves (they will limit skin contact with the environment), use moisturizing cosmetic products, limit the contact of the affected areas with hot water and a rough towel, drink a lot of water that properly moisturizes the skin. You can also support the home treatment of eczema with systemic over-the-counter medications – antipruritic, antihistamines, and analgesics.
Treatment of eczema
If the use of home remedies did not help, you should consult a dermatologist. In medicine, there is no single effective method of combating eczema. Therefore, treatment can be a combination of many treatment methods. The first step to determining the cause of eczema is allergy testing. One way to relieve eczema symptoms is to replace soap with hypoallergenic detergents.
In turn, the most effective methods of skin treatment are creams or ointments with steroids. If the skin changes lead to cracked skin and sores on the hands, dressings containing silver salts may be needed. In more serious cases (skin infection), the doctor may recommend taking antibiotics. Local immunosuppressants and ultraviolet irradiation of the skin are also used to treat eczema. Eczema is a chronic condition, but it rarely becomes severe and requires oral strong steroids.