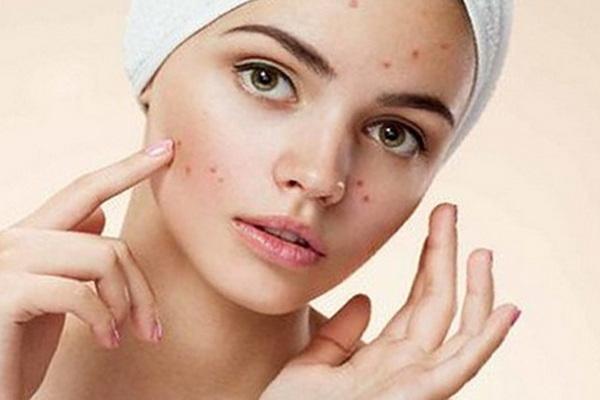
Pimples and acne are a type of skin rash that results from stagnant sebum, keratosis of the hair follicles, and bacterial infection. Acne – what is it, and what types of pimples do we meet?
Pimples appear when an infection of the sebaceous glands is blocked by sebaceous secretions and dead skin cells. A reddish pimple that appears is a lump filled with pus. The most common pimples appear in adolescence, although occasional pimples occur at any age. Acne affects about 80 percent of adolescents and affects 12 percent of women and 3 percent of men after age 25.
Why does acne threaten us during puberty (and also during menstruation)? This is due to a change in hormone production during this period, which leads to the revitalization of the sebaceous glands at the base of the hair follicles. The sticky sebum combined with flaky skin leads to clogged skin pores. It is also easy for bacteria to multiply.
Acne most often appears on the face, back and chest, where we have the most sebaceous glands. They vary in intensity. These can be, for example, small black dots (or black dots) or filled with pus along the edges of the cyst.
Types of pimples:
- Closed black dot, that is, a small pimple left under the skin. We see it as a small fleshy lump.
- An open black dot, clearly visible on the surface of the skin, is black or dark brown (this color is given by oxidizing melanin – a pigment found in our skin)
- lumps protruding from the surface of the skin
- pustules or pus-filled pimples
- nodules that are similar in structure to pa pules, but deeply embedded in the skin, sometimes causing pain
- Cysts are pimples that protrude above the surface of the skin and are filled with pus. They can leave scars.
Causes of acne
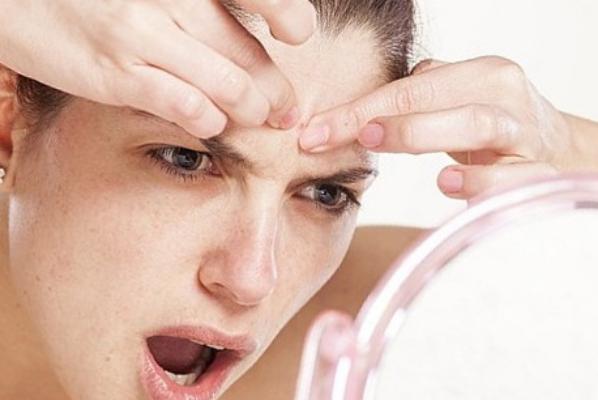

It is not known why some people develop acne so easily and rarely others. How does a pimple appear?
Sebaceous glands are structures found in the pores of the skin, and their job is to lubricate the skin and hair. They secrete sebum, which gets into the hair follicle and the surface of the skin, and earwax. The density of the sebaceous glands in humans is 100-800 per square cm. We find them on the surface of our skin everywhere, except for the hands and soles. Our face and hair have the most sebaceous glands.
If by constantly exfoliating, dead skin cells get stuck in the pores of the skin, they accumulate with sebum and can begin to clog them. This most often occurs during adolescence, when excessive amounts of sebum are produced due to the “violent” hormones, and the skin cannot cope with the excess.
Cells accumulated in the pores of the skin and stuck with sebum begin to block the opening of the sebaceous gland. Problems begin when it comes to bacterial infection. In the vast majority of cases, this is caused by bacteria that naturally occur on the surface of human skin.
An individual’s tendency to develop acne can be associated not only with age, but also with family preferences. It is believed that genetic factors may play a role in the appearance of acne. Other reasons are possible, including carelessness in terms of hygiene, as well as the specific composition of the bacterial flora that lives on our skin.
The increased activity of the sebaceous glands can also be caused by high levels of testosterone and other male hormones.
It is also possible that the condition of the skin in this case is to some extent dependent on a balanced diet, but there is insufficient evidence for this. However, it is worth paying attention to what we eat and switching to foods high in vitamins A, D and E and vegetable fats.
Acne, acne – how to deal with them?
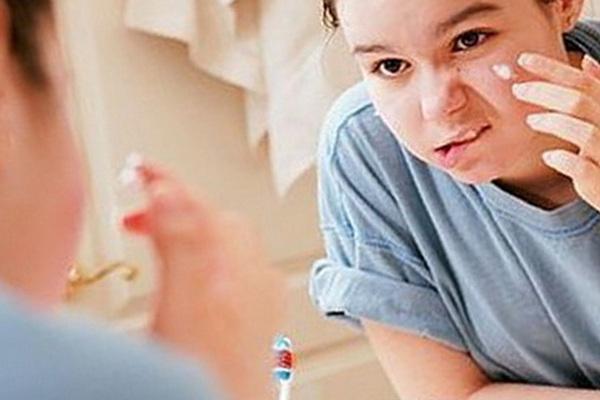

A pimple can develop into pustules or pa pules. In a serious condition, it is necessary to take medications for acne, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. These are medications prescribed by your doctor. Alternatively, over-the-counter medicines such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, adapalene, and various topical antibacterial medications are available. In no case should you squeeze out acne.
Prevention of acne:
- wash your face thoroughly with mild cleansers and water
- skin type care products that do not clog pores
- moisturizing the skin, preferably with odorless products
- drink plenty of fluids
- limiting makeup
- do not touch your face with dirty hands
- avoid stress
- avoid conditioned foods, including dairy