Зміст
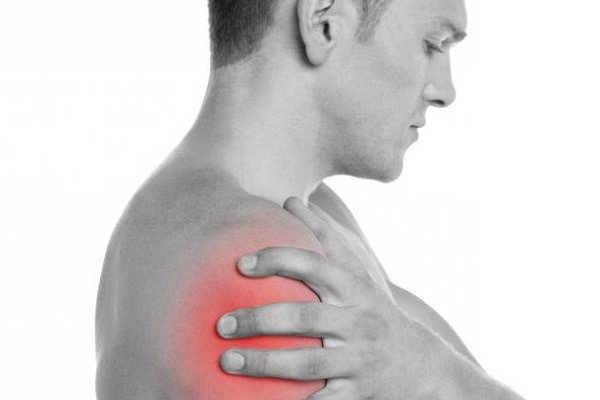
What is Painful Shoulder Syndrome?
The disease is manifested by pain in the shoulder joint with a simultaneous violation of its mobility. PSS most often occurs as a result of orthopedic injuries, diseases of the nervous system, as well as any degeneration of tendon tissue. Generally speaking, pain is caused by damage to various structures of the joints, most often due to improper exercise, too harsh movements, or overexertion.
In special cases, diseases of the heart and lungs, dislocation of the shoulder joint, trauma to the synovial sheaths, fractures of the scapula and clavicle, can cause PSS. Burns that lead to soft tissue contracture can also aggravate diseases. Painful shoulder syndrome is unfortunately quite common and most commonly affects women over 40.
Shoulder pain syndrome symptoms
There is usually a little pain when you try to raise your arms at first. The pain gradually intensifies, and it also accompanies us when we raise our hand. It often appears suddenly and is so strong that it requires us to keep our hand in one position. Other symptoms include increased muscle tension, shoulder swelling, shoulder pain, and even difficulty falling asleep.
Painful shoulder syndrome – treatment
If you experience the above symptoms, see your doctor as soon as possible. He or she will recommend several diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or magnetic resonance imaging. In addition, the specialist will certainly take an interest in ailments, check the limitation of mobility in the joint and possible symptoms of joint inflammation (swelling, redness, warming of the skin around the shoulder).
Treating Painful Shoulder Syndrome
As mentioned, PSS is most commonly caused by muscle overload, tendon injury, or subacial bursitis. What kind of treatment should be followed in these cases?
Muscle overload – the doctor will prescribe painkillers and muscle relaxants, as well as manual therapy.
Tendon Injury – Usually treated surgically, arthroscopically. The aim of the procedure is to repair damaged tendons.
Bursitis – treatment is based on taking anti-inflammatory and pain relievers, as well as steroid injections. Rehabilitation here will also be a necessary step that allows you to fully recover.
Experts say SBP can be cured, although it can be chronic in some patients. It is important to respond quickly, diagnose correctly, and adjust treatment to ensure effective recovery.