Зміст
Chronic skin diseases (dermatoses) are a problem that affects more and more people, including very young people. Eczema, scaling of the epidermis, erythema or itching are the classic symptoms of the most common dermatological diseases. Unfortunately, they usually mostly cover the face, scalp and décolleté, which causes a lot of discomfort. Rosacea, psoriasis, or seborrheic dermatitis are some of the most common and worrying dermatoses.
Their causes have not been established, and it is suspected that they may be the result of autoimmune diseases, genetic factors and environmental factors. However, more and more doctors point out that dermatoses can also occur as a result of constant stress and tension. Check out how the most common chronic skin conditions appear.
Skin diseases: Rosacea
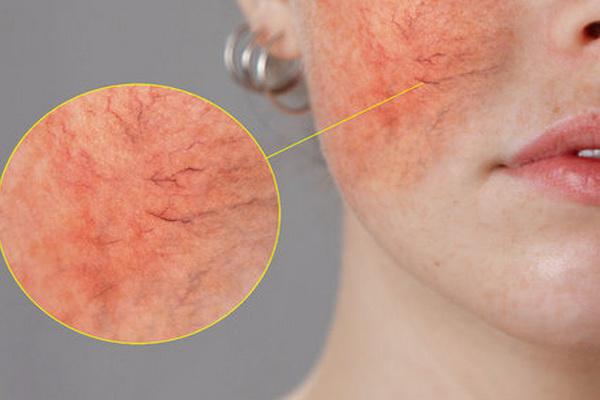
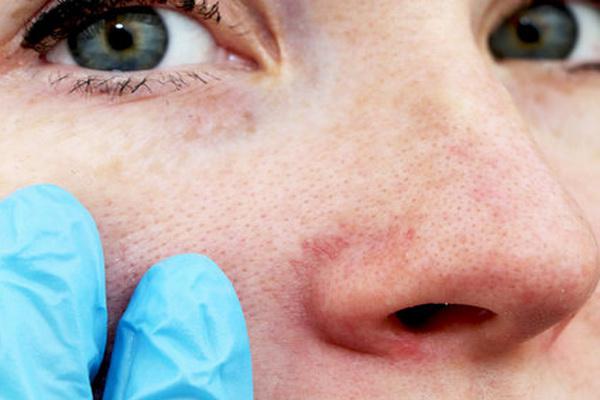
Rosacea is a dermatosis that affects adults, especially those over the age of 30. Typical symptoms are skin redness, papules, spider veins and eczema. They appear mainly on the face, neck and décolleté, very rarely on the scalp. The causes of the disease have not yet been identified, and there are suspicions that they are influenced by genetic factors, hormonal and vasomotor disorders.
People with fair complexions and rosacea are more likely to develop rosacea. It also accompanies diseases of the digestive system, especially stomach and duodenal ulcers, and food intolerances. Another risk factor is UV radiation, rapid temperature changes, bacterial and viral infections. Treatment is based on the use of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and blood circulation drugs.
Skin diseases: Seborrhea dermatitis
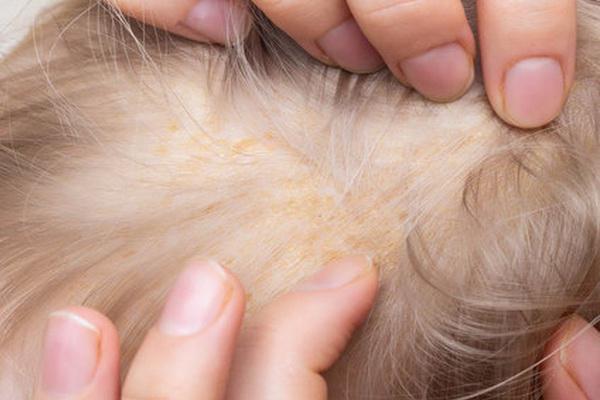
Seborrhea dermatitis (PsA) is up to 10 percent. It manifests itself in the form of erythematous exfoliating changes on the face, scalp, décolleté and skin folds. Their cause is excessive seborrhea. The skin is red, then covered with oily yellow scales. They are accompanied by slight itching. The disease causes inflammation on the scalp and can cause alopecia. PsA can be caused by hormonal and immune disorders (including decreased immunity), genetic predisposition, prolonged stress, and fungal and yeast infections. Symptoms are also aggravated by unhealthy diet and alcohol abuse, and are more onerous in the fall and winter and disappear in the summer for many.
Skin diseases: Atopic dermatitis
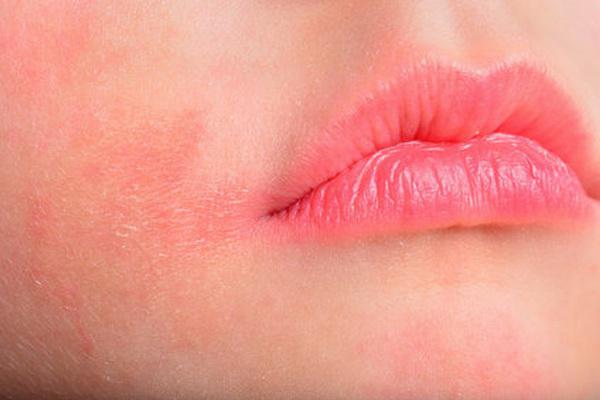

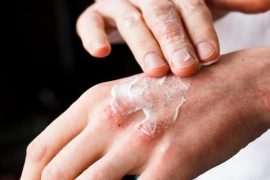
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common and unpleasant skin condition that usually manifests itself in early childhood. The characteristic symptoms are red and scaly eruptions and severe itching. However, the first symptoms are excessively dry and rough skin, only after a while, inflammatory foci begin to form – usually on the face, gradually spreading to the rest of the body. Atopic dermatitis is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental and immunological factors.
The patient’s psyche also has a great influence on the development of the disease – chronic stress aggravates the symptoms. Atopic dermatitis is closely related to a dysfunction of the immune system (hence inflammation of the skin caused by overreacting to allergens) and is often associated with other conditions such as bronchial asthma or food allergies. Treatment consists of emollients, that is, drugs that restore the lipid layer of the epidermis, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs. In severe flare-ups, antibiotics and even immunosuppressant are required to suppress the overactive immune system.
Skin diseases: Psoriasis
Psoriasis is another skin condition with a strong tendency to relapse. It is caused by genetic and immunological factors. However, bacterial and viral infections, as well as diabetes and gout, contribute to it. Disease outbreaks usually appear on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and the face and scalp. At first, these are red-brown lumps, which are then covered with silvery scales. In the place of their exfoliation, the skin becomes smooth and shiny (the so-called stearin suppository symptom). The disease also affects the nails, less often the joints (it causes inflammation and can lead to degeneration and even disability). Treatment requires special cleaning of the skin, as well as the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, steroid ointments and immunosuppressant.