Зміст
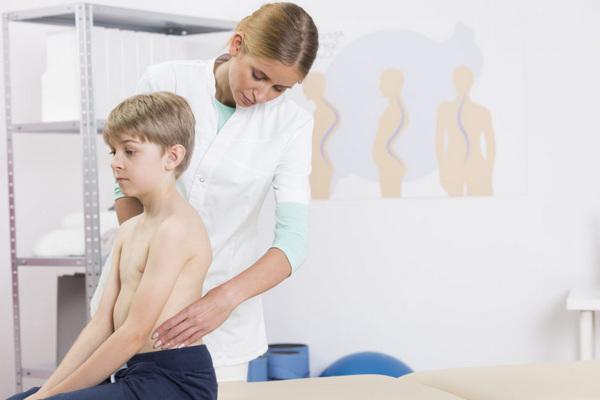
Posture defects in children are now considered a problem of civilization. The hours spent at the desk, and then in front of the TV screen or computer, too high-calorie diet – these are the main factors contributing to their formation. Can posture defects in children be prevented? Yes! Read about how to do this in our article.
What is body posture?

Posture is an individual feature of each person. It’s really hard to define. Generally speaking, by posture, we mean: “the individual shape of the body and the position of individual parts of the trunk and legs in a standing position.” The position of the body is correct, if the head is straight, all physiological curves of the spine (lordosis and kyphosis) are preserved, the pelvis rests on the femoral head, the legs are straight, and the feet have regular dimples and protrusions. If deformity occurs in any of these areas, it is a defect in posture.
The position of the body is formed over the years and is influenced by many factors – the environment in which we live, the condition of muscles, bones, joints and ligaments, the functioning of the nervous system, and even will and emotions.
Why do posture defects mainly affect children?
The periods when a person is most susceptible to defects in posture are called critical periods. The first such period usually occurs at the beginning of school, that is, when the child is 6–7 years old. The other is during the spike in puberty. Why, then? Because this is the time of the child’s greatest growth – his torso, upper and lower limbs and feet are greatly lengthened. As a result, muscle and ligament tension is temporarily reduced, and the center of gravity changes, shifting upward. You must remember that when a child goes to school, the child’s life also changes dramatically. From now on, instead of running and jumping freely, he must carry a heavy backpack, sit at the school desk for several hours, and then do his homework at home.
How common are posture defects?
A flat or sunken chest, scoliosis, a rounded back, a prominent abdomen, or flat feet are the most important examples of poor posture. Improper sitting posture, little physical activity and improper wearing of a backpack play a huge role in their development.
Round back, scoliosis, valgus knees, flat feet are the most common childhood disorders
- Round back, or thoracic hyperopias, is a defect in posture that affects the thoracic spine. This defect is characterized by a deepening of one of the natural curves of the spine – thoracic kyphosis. A round back can appear in a child as a congenital or acquired defect. What is the immediate cause? A round back can occur with diseases such as rickets, tuberculosis, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), or Scheuermann’s disease. Rounding of the back can also occur as a result of muscular dystonia, a condition in which a group of muscles contracts and stretches. In addition, poor habits, such as poor posture while sitting or immobility, can also cause muscular dystonia. This problem also often occurs among teenage girls who, ashamed of their lush breasts or tall,
- Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine, in which the vertebrae also rotate and bend. This is a very serious and at the same time the most common, along with a round back, posture defect in children and adolescents. Scoliosis in girls occurs several times more often than in boys, and has three stages of development. Scoliosis usually changes the appearance of a child’s body. Possible deformation of the torso and asymmetry of the waist, a protruding shoulder blade or lowering of one of the arms (oblique position). Untreated scoliosis can have far-reaching health consequences, including: contributing to neurological damage, circulatory and respiratory problems.
- Hal lux valgus is a defect in the lower extremities where the baby’s knees are aligned inward. How can I tell if my child’s knees are crooked? If in an upright position, the knees are brought together (“looking at each other”) and there is a clear gap between the feet. A child’s knees can become crooked for a number of reasons, including being overweight or obese, growing quickly, decreased muscle tone, and flat feet.
- Flat feet are a deformity of the foot in which the natural arches of the foot are lowered. In addition, deformation of the calcaneus is also observed. A child with flat feet gets tired faster and often complains of pain in the feet. Flat feet are the result of weakening of the muscle groups that hold the arches of the foot. The occurrence of flat feet in young children is a completely natural phenomenon caused by the presence of fat pads. Only at 3–4 years old, the arches begin to gradually become noticeable. The foot takes the correct shape by about 6 years. If this does not happen, an appointment with a specialist is required.
Posture defects – what are their consequences
Posture defects, especially those resulting from abnormal physiological curvature of the spine, can cause many ailments. They can also disrupt the body’s most important systems, including the respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems. For example, a deepening of cervical lordosis will cause headaches, dizziness, or numbness in the hands. In turn, deepening of the thoracic kyphosis can lead to shallow breathing and weakened ventilation.
This will happen because with chest hyperphorias, the chest will no longer expand so freely. On the other hand, raising any of the physiological curves of the spine will transmit the vibration that occurs during walking to the skull, causing chronic headaches, for example.
Prevention of posture defects in children
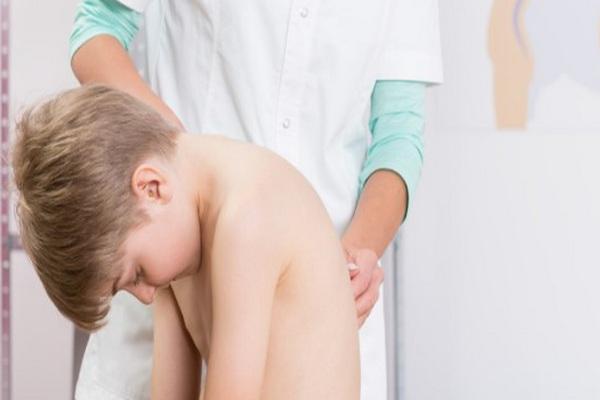
Postural defects can and should be prevented. It is best to introduce prophylaxis at school age. Then there is a better chance that the child will protect himself from the most serious defects in posture. The key to prevention, for example, is the correct wearing of the schoolbag. Its weight should not exceed 10-15% of the child’s weight. The backpack should also have a reinforced back wall and wide shoulder straps. The child should always wear it on both shoulders.
Another important issue is encouraging children to be physically active. Of course, the type of this activity must be adapted to the individual capabilities of the child, his interests and the existing defect in posture (if any). The choice of footwear is also critical for the child’s posture. A baby who is just taking the first steps should be allowed to walk barefoot as much as possible. When going outside, they should wear shoes that support the heel and have a stiff sole.