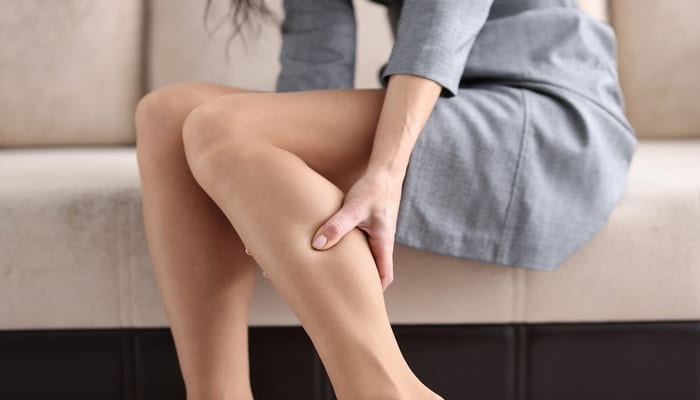
People experience pain in the legs at different periods of their lives, but this topic becomes especially relevant and problematic among the elderly.
With age, the joints, muscles, and blood vessels of the body can undergo wear and tear, which often leads to pain and discomfort when walking.
In this article, we look at the causes of foot pain in the elderly, methods of diagnosis and treatment, as well as practical recommendations for foot care and discomfort prevention.
Why do legs hurt when walking in old age?
Foot pain in the elderly can be caused by a variety of factors, and it is important to distinguish between them in order to find the right treatment and care. Consider the most common reasons:
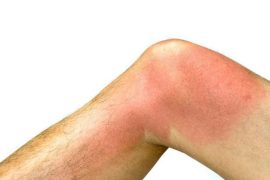
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints that can cause pain, morning stiffness, and limited mobility. These conditions can significantly impair the quality of life of the elderly.
- Flat feet: Flat feet is a condition in which the normal architecture of the foot is lost, which can lead to leg pain and fatigue when walking.
- Vascular problems: older people are at risk of developing peripheral arterial disease (PAD). In this case, the narrowing of the arteries in the lower extremities can lead to pain, cold, and numbness in the legs when walking.
- Diabetic neuropathy: Diabetes can damage the nerves, which can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the legs.
- Injuries and fractures: The possibility of injuries and fractures increases with age. Even small injuries can cause pain and discomfort when walking.
- Bad shoes: Wearing the wrong shoes can cause foot pain. Shoes that are uncomfortable, too tight, or tight can cause pressure and friction, leading to discomfort.
Why do legs hurt: Diagnosis and treatment
To effectively treat leg pain in the elderly, it is necessary to determine its source. This may require a doctor’s consultation and additional studies, such as x-rays, ultrasound, angiography, and others.
Treatment for leg pain will depend on its cause:
- Arthritis: Treatment for arthritis may include anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, orthotics, and joint injections.
- Vascular problems: In the case of PAD, surgery or procedures may be required to restore normal circulation.
- Diabetic neuropathy: Blood sugar management, physical therapy, and medications can help relieve pain and discomfort.
- Injuries and fractures: Treatment includes fixation of fractures, rehabilitation