Зміст
Venous thrombosis, commonly called phlebitis, is one of the diseases that manifests itself in the least characteristic way. Fatigue, minor breathing problems and pain in the limbs disturb the patient in the early stages of the disease. We often downplay these symptoms, allowing the disease to develop. How is thrombosis manifested, when to see a doctor, and how to prevent it?
Most important disease information
Venous thrombosis is a thromboembolic disease, also called thrombophlebitis. These affects people of all ages, giving few characteristic symptoms. Most often this happens in people over sixty years old, usually affects women. What is the disease about? Different types of blood clots form in the veins, which disrupt the blood flow and the cardiovascular system. If thrombosis is not detected at the right time, this can lead to significant health difficulties and may even be life-threatening. Let’s look at the factors contributing to this disease and its characteristic symptoms.
Moments that contribute to the development of thrombosis?
The most frequently mentioned factors contributing to the development of thrombosis are:
• overweight and obesity;
• diseases requiring immobilization;
• no movement;
• heavy smoking;
• hormonal drugs;
• use of contraceptives;
• crayfish.
How is thrombosis the most common?
Thrombosis gives not very characteristic symptoms. They often resemble ordinary fatigue or the common cold. The patient underestimates them, which allows the disease to develop. The most famous manifestations of thrombosis are:
• cough, shortness of breath – blood clots in the pulmonary artery obstruct the flow of oxygen, which leads to increased heart rate and difficulty breathing;
• irritability, poor mood – caused by a violation of blood circulation;
• constant fatigue – this is the result of the accumulation of blood clots in blood vessels. As a result, the body becomes weaker, and we feel more tired;
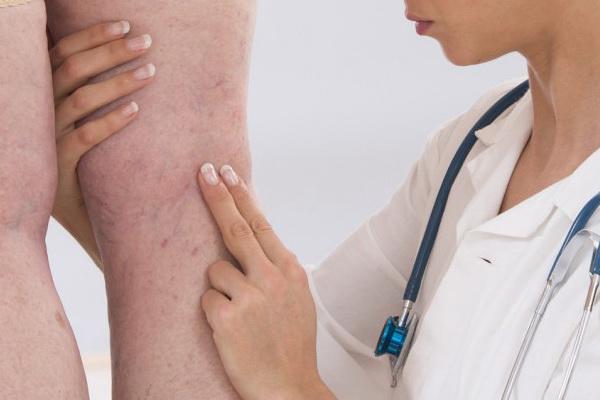
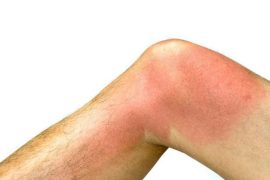
• swelling of the extremities – usually occurs when blood clots occur in deep veins. Swelling of the extremities can interfere with the proper flow of blood and oxygen to the heart, lung, or brain;
• pain in the limbs – they usually appear in one place and resemble stitching pains. They are especially worried when walking and flexing their limbs;
• fever – usually occurs when a clot lags behind the wall of a blood vessel and enters the bloodstream.
Thrombosis treatment?
The type of treatment for thrombosis depends on the severity of the disease and the location of the clot. Conservative therapy is usually used, which includes the administration of anticoagulants, reducing the formation of blood clots and stopping the formation of more. Clots are also removed surgically. The treatment of thrombosis lasts a long time. This requires patience and dedication on the part of the patient.
How to prevent thrombosis?
You can prevent venous thrombosis by leading a healthy lifestyle and, above all, by following a healthy diet. The menu should be rich in foods containing vitamins B3, C and E, as well as iron, zinc and manganese, which improve blood circulation. Easily digestible and low-calorie foods are recommended. Physical activity, which helps maintain a healthy body weight, is also important. You should definitely quit smoking.
What complications can cause thrombosis?
• relapse of thrombosis;
• complete occlusion of veins, which can lead to edema, shock and renal failure;
• pulmonary embolism – leads to pulmonary failure;
• post-thrombotic syndrome – leads to heart failure and ulceration of the veins.
Venous thrombosis is a dangerous disease that requires immediate intervention and appropriate treatment. Therefore, it is worth observing the symptoms and leading a healthy lifestyle.