Зміст
Mumps is a colloquial term for common mumps, an illness caused by infection with the mumps virus. An inherent symptom is a painful swelling of one or both of the parotid glands. This ailment is included in the so-called childhood diseases, but there are cases of mumps in adults. How can you get mumps? Are there ways to protect against this disease?
Mumps is a highly contagious infectious disease
Mumps, or mumps, is a viral disease caused by the mumps virus, which affects the parotid and other glands, and sometimes the nervous system.
The disease occurs exclusively in humans. You can become infected by inhalation through contact with respiratory secretions, which are passed on by coughing and sneezing. They mainly affect children with mild illness, but there are many cases of mumps among adolescents and adults. There are cases when a patient requires hospitalization due to complications of the disease, the most common of which are meningitis, pancreatitis or orchids. Almost anyone who has not been vaccinated against the disease can get mumps. It is estimated that about 1/3 of those infected are asymptomatic, and only 30-40% will develop characteristic symptoms.
How does mumps manifest?
Patients with mumps can develop a wide range of symptoms, the first of which occurs between 12 and 25 days after exposure to the mumps virus. In the early stages of the disease, the patient may complain of malaise, muscle aches and headaches, neck stiffness, increased fatigue, decreased appetite and mild fever, which are typical symptoms of the flu. Over time, they gain strength, manifesting in:
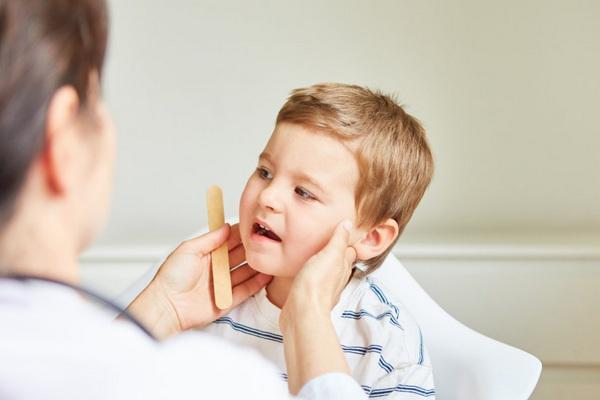
- visible swelling and soreness of the parotid salivary glands, which are affected sequentially or simultaneously (edema under the mandibular and sublingual glands is rare);
- Ear ache;
- catarrh of the upper respiratory tract;
- Difficulty opening your mouth, chewing and swallowing food;
- dry mouth;
- fever even reaches 39 degrees Celsius.
Swelling of the parotid glands most of all worries the first 2–3 days, then gradually subsides. The patient is contagious to the environment about 1–2 days before the onset of swelling of the salivary glands, and even 9 days after the onset of the first symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment of mumps
If you have any bothersome symptoms that may indicate mumps, see your GP or pediatrician. (for a child). The diagnosis is usually made on the basis of an interview and clinical examination. This is an important procedure that allows your doctor to determine the cause of your salivary gland.
Treatment of mumps is symptomatic. In order to reduce fever and reduce pain caused by salivary gland enlargement, drugs based on paracetamol or ibuprofen.
For children, these products work best in the form of syrups (for example, Paracetamol, Nurofen for children) or suppositories (for example, Baby Boom, Efferalgan). Often, relief can be achieved by warming the sore spots, wearing a soft scarf around your neck, warm compresses, or applying a warming ointment (e.g. Aromactiv + gel, Rub Arom, Vicks VapoRub). It is advisable that the patient remains isolated from healthy people when infection is most likely.
Dysfunction of the salivary glands means less saliva is produced, so remember to irrigate your body regularly and rinse your mouth. Sour foods can make pain around your salivary glands worse, so it’s best to avoid them when you’re sick. Warm compresses can help relieve painful symptoms.
Complications of mumps in adult patients
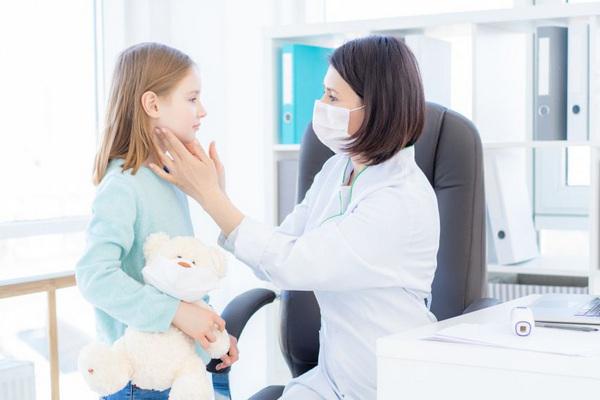

Mumps infection is usually mild, especially in younger patients; however, complications that affect adolescents and adults cannot be ruled out. Meningitis occurs in 1 in 10 patients, several times more often in boys. Other complications include:
- inflammation of the middle ear or auditory nerve, which can ultimately lead to hearing loss;
- inflammation of the eye, heart muscle, joints;
- inflammation of the testicle and epididymis, which occurs in 15-35% of boys after puberty and adolescents (can lead to infertility);
- inflammation of the pancreas, which is more common in women;
- inflammation of the thyroid gland, mammary glands, prostate, ovaries.
Complications of mumps in adult patients
is especially dangerous for pregnant women. Infection with the virus in the first trimester of pregnancy is fraught with miscarriage. Adults can get vaccinated – getting measles, rubella, or mumps is not a contraindication to getting vaccinated.