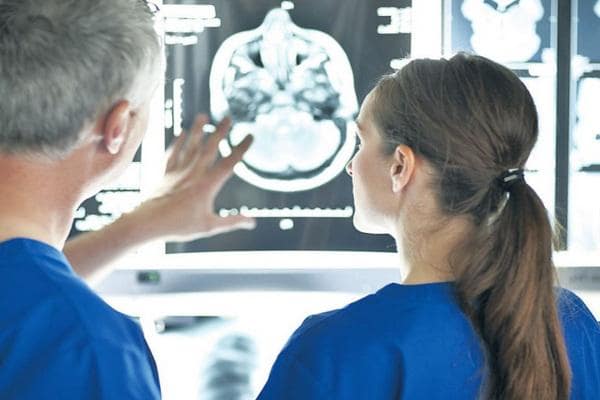
A stroke is an “attack” that occurs when blood circulation is disturbed in any part of our brain. It is the fourth leading cause of death in the world and one of the most common causes of disability among adults.
Strokes are of two types: ischemic and hemorrhagic. The first type includes strokes that occur when blood flow to the brain is restricted or blocked. The second type includes strokes that result from hemorrhage in a specific area of the brain.
The type of stroke determines its symptoms
- All warning signs appear suddenly, and some of the most common are:
problems with coordination, loss of balance or control over our body movements. - Difficulty speaking clearly and having difficulty understanding other people’s speech.
- Numbness in the arms, legs, or face, especially on one side.
- Other common symptoms include: complete paralysis, vision problems in one or both eyes, sudden feeling of confusion or confusion for no apparent reason, sudden restlessness or unexplained restlessness.
A short examination will help to correctly identify a stroke. Do them one by one.
Face: The face should be examined for complete or partial paralysis of the facial muscles, and the person suspected of having a stroke does not lose sensitivity to the face. For example, you can ask the patient to smile. If it’s not symmetrical or different from what we usually see, it could be a sign of a stroke.
Hands: Ask the person you suspect of a stroke to stretch out their arms in front of you and see if any of them falls limply.
Speech: Ask the person to repeat a longer phrase and make sure the speech is clear and understandable.
Timing: Every minute after a stroke is extremely important, you should call an ambulance as soon as possible.
You must remember that warning signs come on quickly and start suddenly, so don’t wait for your condition to improve. If you notice the above symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible and call an ambulance.
Moreover, even if you experience these symptoms, which disappear after a few minutes, you should see your doctor. These short-term changes may represent transient ischemic attacks and may indicate an increased risk of complete stroke in the near term.
In some cases, people can confuse the symptoms of a stroke and a migraine, so here’s how to tell the difference: The early symptoms of a stroke come on suddenly, while with a migraine, symptoms develop gradually and get worse.
Sometimes migraine symptoms manifest as irritants such as flickering lights or optical illusions. In contrast, stroke symptoms usually begin with the loss of certain abilities, such as hearing loss, loss of vision, and loss of strength in the limbs.
You should be aware that stroke can occur at any age, but there are factors that can increase your chances of developing one. These are: high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, heart disease, frequent migraines, genetic factors.








